The Communication Infrastructure of the Future
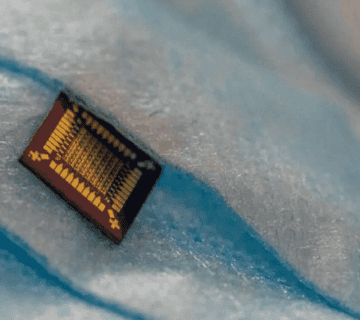
Flexible antennas, particularly those fabricated using silver and copper materials, are at the forefront of advancing NFC (Near Field Communication) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technologies. Recent advancements in fabrication methods and material science have significantly improved the performance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of these antennas, enabling their widespread adoption across various industries.
Flexible Antenna Technologies
Flexible antennas are primarily constructed on substrates such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or paper, utilizing conductive inks containing silver or copper nanoparticles. These materials strike an ideal balance between flexibility, conductivity, and affordability. For example, a study demonstrated the fabrication of a flexible RFID antenna through an environmentally friendly additive manufacturing process, resulting in copper electrodes with resistivity comparable to commercial silver thick-film electrodes. Such innovations highlight the potential of flexible antennas to deliver efficient and sustainable communication solutions.
Fundamentals and Applications of NFC Technology
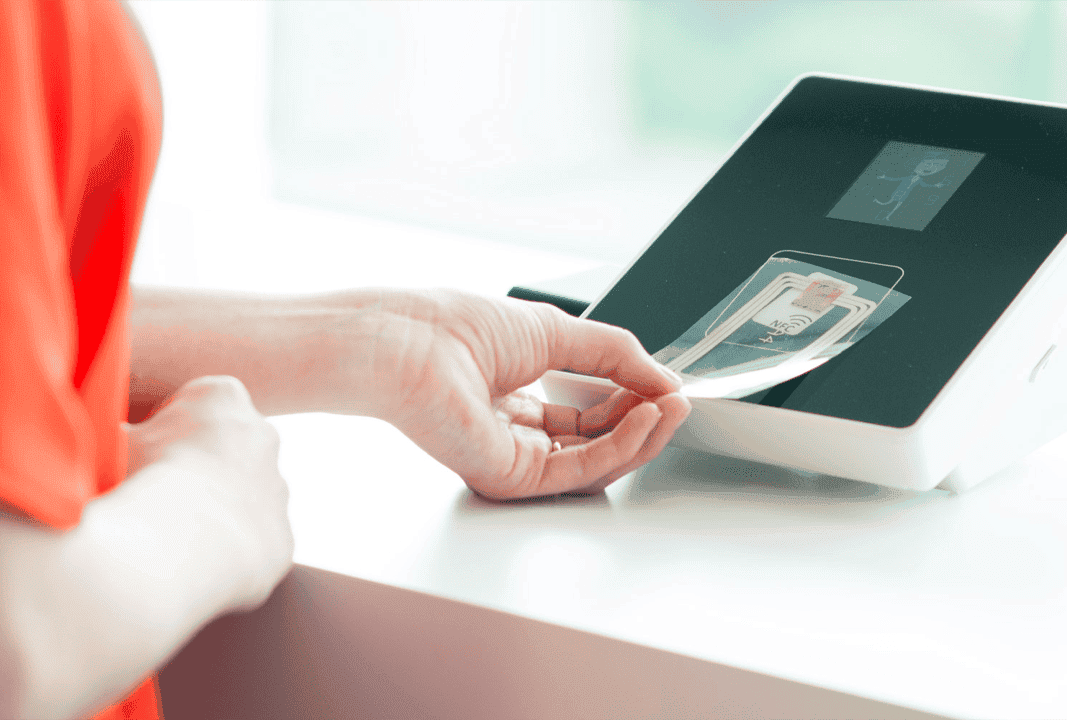
NFC technology facilitates short-range wireless communication, typically operating at a frequency of 13.56 MHz. The design of NFC antennas requires meticulous attention to size and flexibility to ensure consistent performance under varying conditions. Research into flexible silver-printed NFC tag antennas has focused on addressing challenges related to miniaturization and the effects of bending, ensuring reliable communication across diverse applications such as contactless payments, smart cards, and wearable devices.
RFID: Smart Tracking and Data Collection
The integration of flexible antennas into RFID systems has revolutionized data collection and asset tracking. These antennas can be seamlessly incorporated into various surfaces and materials, offering versatile and efficient solutions. The use of silver and copper-based inks for printing RFID antennas has been extensively explored, with studies comparing their performance on cost-effective substrates. These studies emphasize the potential for low-cost, high-performance RFID and NFC antennas in microelectronic measurement systems, further advancing the capabilities of smart tracking technologies.
Applications and Future Perspectives
The adoption of flexible antennas in NFC and RFID technologies spans a wide range of industries, including healthcare, logistics, consumer electronics, and automotive sectors. Innovations in fabrication techniques, such as inkjet printing and additive manufacturing, are driving the development of more efficient, durable, and cost-effective flexible antennas. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing material properties, such as conductivity and flexibility, while enhancing antenna designs to meet the growing demands of modern communication systems.
Flexible antennas, with their use of silver and copper materials, are pivotal to the continued evolution of NFC and RFID technologies. Through sustained research and development, these antennas will achieve greater performance, durability, and affordability, enabling their application in a broader range of industries and contributing to the advancement of next-generation communication infrastructures.